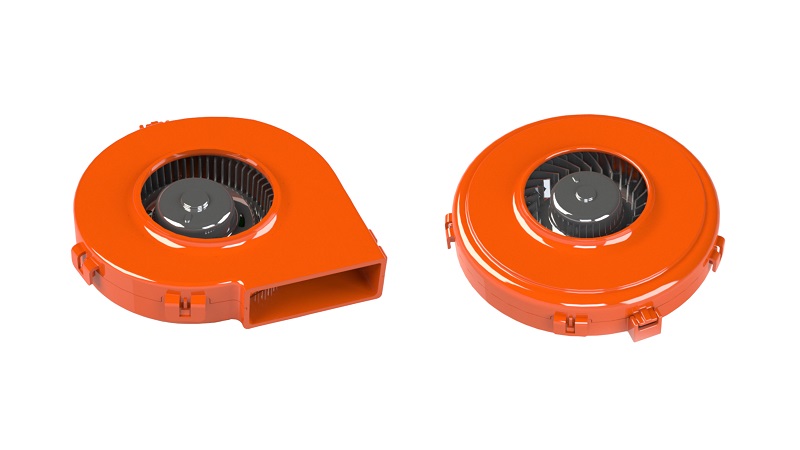
Applications for blower motor
-
Automotive
-
Automotive seat ventilation system
28 Jun. 2022
Blower motors have various applications in cooling devices, electric equipment, and air circulation. They are commonly installed in computers, automobiles, and industrial equipment like manufacturing plants, transportation machines, and ventilation systems. Blower motors facilitate air intake, suction, transportation, dust extraction, ventilation, blowing, aeration, drying, and cooling processes in different settings.
The following chapters introduce the types and applications of blower motors in various fields.
- Classification of blower motor types
- What are applications for blower motors?
- Example applications in industrial equipment
- Example applications in commercial products
- Example applications for automotive
- Identifying applications of blower motors
- Overcoming your problems with ASPINA's advanced blower motor technology
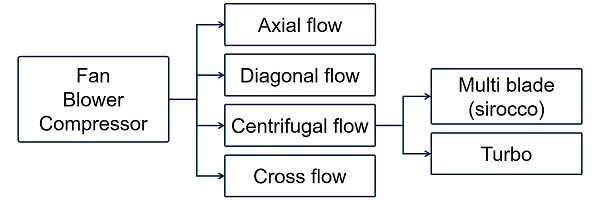
Classification of blower motor types
Blower motors (blowers) are classified into four types: axial, diagonal, centrifugal (radial), and cross flow.
Axial flow types have blades that moves air parallel to the shaft on which the blades rotate. In diagonal flow blowers, the impeller is inclined at a constant angle with respect to its axis of rotation, and air also flows in the same direction. Centrifugal flow blowers use the centrifugal power supplied from the rotation of impellers to increase the kinetic energy of air. Centrifugal blowers can be further classified into two types according to their structure: multi blade (sirocco) type and turbo type. Cross flow blowers suck in air from one radial direction of the impeller and blows it from a radial direction of about 90°.
What are applications for blower motors?
A blower motor is mainly used for cooling devices, electric devices, and air circulation inside an equipment. It is also installed in specific places where there is heat. For example, in computers it is installed in the CPU or power supply, and in automobiles it is installed in radiators, air conditioning condensers, and air intercoolers.
Blower motors are used in various industries, and are built into equipment such as transportation machines, or equipment for processing, assembly, and packaging. They are also found in products such as computers and home appliances, where they facilitate size reduction and performance enhancement.
Example applications in industrial equipment
- Air intake
- Air intake at manufacturing plants where machinery such as presses or welding machines are used
- Suction
- Suction to hold objects in place at food, textile, and other such manufacturing plants
- Vacuum gripping
- Suction for vacuum packing vegetables or to hold and lift paper or other processing materials
- Transportation
- Transportation in equipment such as pneumatic tubes or powdered material transporters
- Dust extraction
- Dust extraction at manufacturing plants where grinding is performed or powdered materials are used
- Ventilation
- Ventilation at worksites, trains, clean rooms, etc.
- Air supply
- Supply of air to gas burners, incinerators, or medical equipment such as CPAP
- Blowing
- Blowing for pipe cleaning, sandblasting, etc.
- Aeration
- Aeration of septic tanks or oxygen supply to aquaculture ponds
- Drying or cooling
- Drying or cooling processing materials on a production line
Example applications in commercial products
- Air brushes
- Vacuum cleaners
- Hair dryers
- Air conditioning
- Humidifiers
- Ventilation fans
- Water heaters
- Cutting plotters
- Copiers
- Printers
- 3D printers
- Air purifier
- Telecommunication equipment
- Medical equipment
- Home fuel cells
- Servers
- Personal computers
- Projectors
- Leaf blowers
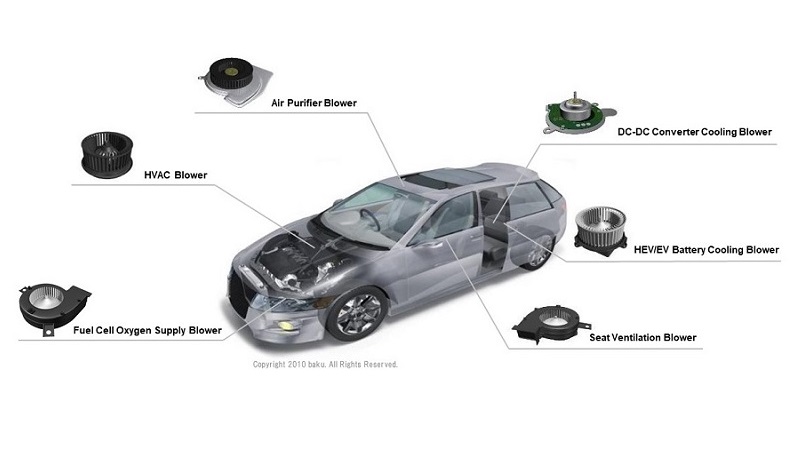
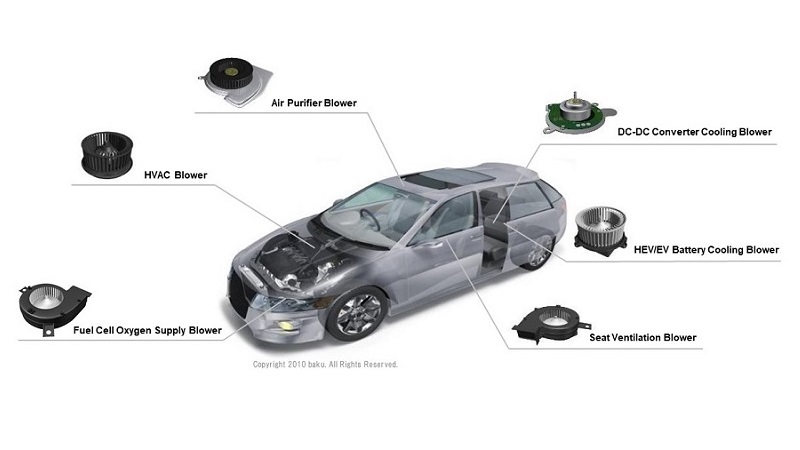
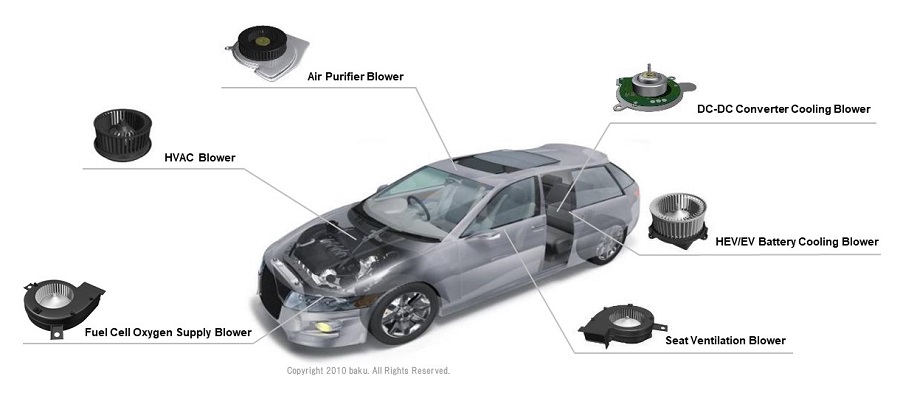
Example applications for automotive
- Seat ventilation blower
- Usually built in to the seat cushion and backrest, and draws air from vehicle cabin to seat.
- Seat heating/cooling blower
- Pushes air out directly and circulates the air throughout the seat surface.
- DC-DC converter cooling blower
- HEV/EV battery cooling blower
- Fuel cell oxygen supply blower
- Air purifier blower
Identifying applications of blower motors
The blower motor is an optimal device for blowing and cooling, and is used in a variety of equipment around us. They range from the large blowers found in applications such as production machinery and clean rooms, to the small blowers built into devices such as home appliances or personal computers, and are used to move air for exhausting ventilation or cooling.
Overcoming your problems with ASPINA's advanced blower motor technology
The key to blower motor development is to study the electric motor, fan, casing, impeller, circuitry, and other components in detail to build up an accurate understanding of where performance losses occur. ASPINA draws on their expertise built up through many years of development, not only to optimize blowers or their motors to improve their performance, but also to make them smaller, lighter, have longer operating times. The vibration and noise level are reduced to low levels, using our accumulated manufacturing experience and know-how. Along with providing greater flexibility in product design, ASPINA’s blower motors can help reduce costs. ASPINA also has extensive scope for customization, so please don't hesitate to contact us.
If you have any questions or would like samples, quotations, consulting on customization etc., please feel free to contact us from our form.
Related information
List of the same series columns
- What is a blower motor?
- Advantages of brushless DC motors over brushed DC motors
- Features and applications of DC motors
- Is this brushless motor cheap or expensive? - What factors determine its price?
- Different types of DC motor and their respective features
- What is a geared brushless DC motor?
- How does an electronic speed controller for a brushless DC motor work? And what should you consider when you choose the right one?
- Small brushless motors
- Difference between brushed motor and brushless motor
- What are the disadvantages of brushless DC motors? And how can they be overcome?
- Advantages of brushless DC motors: How they differ from brushed DC motors
- What is an actuator?
- How do brushless DC motors work? The need for a drive circuit explained
- Do brushless DC motors require a drive circuit? – Controlling brushless DC motors
- What is a brushless DC motor?
- How do brushed DC motors work? The need for regular maintenance explained
- Brushless DC motor applications: examples that demonstrate their features
- Stepper motor applications: Examples that demonstrate their features
- Motors designed for easy control: How do stepper motors work?
- What are the differences between brushed and brushless DC motors?
- What is a PSC motor
- What is a servo motor?
- What is a blower?
- What is a DC motor? - features and mechanisms
Contact us for more information
- New inquiry
- Prototype
- Upgrade
- Customization
- Your spec
- Literature
- Support
- Others