Features and applications of DC motors
-
Automation
-
Health & wellness
-
Life environment
-
Automotive
10 Feb. 2022
Electric motors can be broadly divided into AC and DC motors. The two types of motors have different characteristics, with DC motors being widely used in daily life. Why is it that DC motors are so common? How do the two types of motors differ? This article considers the benefits of DC motors and their applications.
Differences between AC and DC motors
The simple explanation of the difference between the two types is that DC motors run on direct current (DC) power supply and AC motors on alternating current (AC) power supply. In a DC power supply, the positive and negative polarities remain fixed. In an AC power supply, in contrast, the polarities cycle between positive and negative with a fixed cycle time. While both types of power supply can be used to rotate a motor, their differences influence the motor’s power, speed, and ease of control.
Benefits of DC motors
DC motors are widely used in daily life. Why is this?
Steady rotation characteristics with respect to voltage
Control of DC motors is easier because of their simple design, which comes about because the current from a DC power supply always flows in the same direction. As a result, the motors benefit from steady rotation characteristics while still being able to respond sensitively to changes in supply voltage. As the polarities of an AC power supply cycle between positive and negative, using one to drive a DC motor would only result in its vibrating backwards and forwards.
Ability to use portable power supplies
The familiar dry-cell battery is one example of a direct-current power supply that could be used to drive a DC motor. A slightly larger example would be the batteries used in cars. This ability to use portable power supplies is one of the advantages of DC motors.
Even more familiar perhaps are the conventional electricity wall sockets that provide an AC power supply. Most home appliances run on this AC mains power. Put another way, AC motors are not suitable for use in daily life in those situations where no mains power supply is available.
Low cost
Some DC motors can be driven by a single dry-cell battery providing only 1.5V. Being able to operate at such low voltages and with simple control hardware allows for a low cost.In contrast, AC motors operate by plugging into the mains power supply. That is, they operate at voltages of 100V or more. The control equipment required for steady drive operation is also more complex, meaning they are not as easy as DC motors to incorporate at low cost.
Ease of miniaturization
The vibration functions of mobile phones are one example use of DC motors. DC motors also drive the electric fans in laptop computers. Small DC motors less than 1 cm in length are already found in a wide range of familiar products.
Applications for DC motors
Applications for DC motors are scattered across our daily lives. Let’s consider some of the different uses for these motors.
Computer equipment
Uses include CPU cooling fans and the drive motors for HDDs and CD-ROM drives. These applications commonly use brushless DC motors to avoid problems with the dust given off by wear of the motors’ brushes and commutator.
Audio and video equipment
DC motors are also used in audio and video equipment, including in audio CD, DVD, and Blu-ray players.
Home appliances
DC motors are used in mini 4WD and other radio-controlled models, to drive electric toothbrushes or shavers, and in small electric fans. Products like these use small DC motors that operate at low voltages of around 9V.
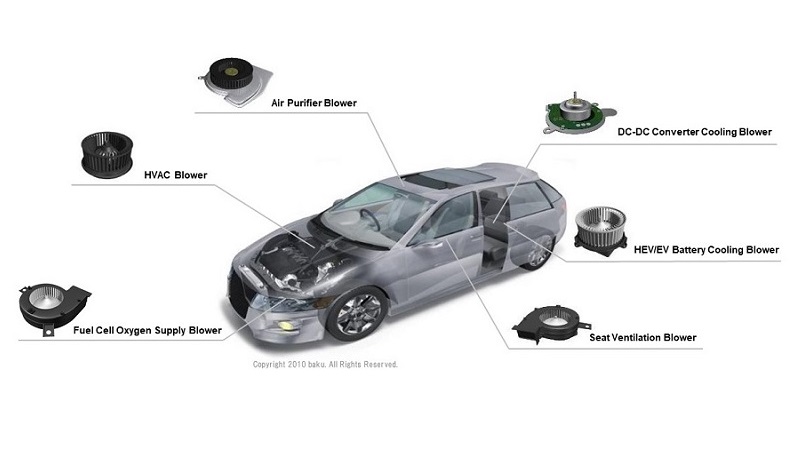
Automobiles
Vehicles use large numbers of DC motors in applications such as wiper motors, power seat motors, and power window motors.
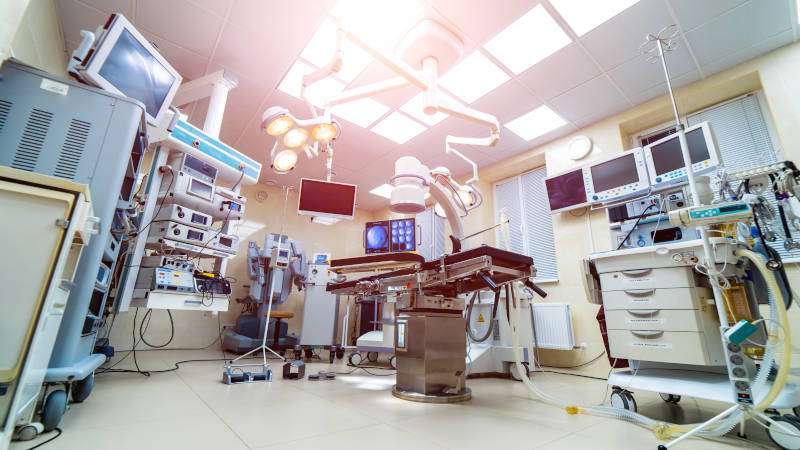
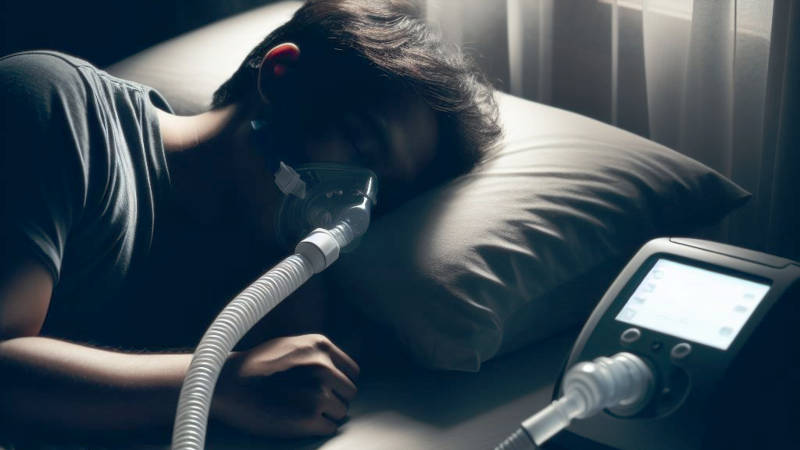
Industrial machinery and medical equipment
Large numbers of DC motors are used as servo motors in industrial robots. Medical equipment applications include fan motors in respirators and oxygen concentrators. They are also used in agricultural and construction machinery.
Wide range of areas where DC motors are used
While electric motors are used in a wide range of electrical products, they are divided into two main types, AC and DC motors, which use different power supplies. Each type has its own particular advantages and disadvantages, with their respective features being utilized to achieve the desired performance in the equipment in which they are used.DC motors in particular are used in a wide range of applications and can be found in many familiar electronic products.
List of the same series columns
- Applications for blower motor
- What is a blower motor?
- Advantages of brushless DC motors over brushed DC motors
- Is this brushless motor cheap or expensive? - What factors determine its price?
- Different types of DC motor and their respective features
- What is a geared brushless DC motor?
- How does an electronic speed controller for a brushless DC motor work? And what should you consider when you choose the right one?
- Small brushless motors
- Difference between brushed motor and brushless motor
- What are the disadvantages of brushless DC motors? And how can they be overcome?
- Advantages of brushless DC motors: How they differ from brushed DC motors
- What is an actuator?
- How do brushless DC motors work? The need for a drive circuit explained
- Do brushless DC motors require a drive circuit? – Controlling brushless DC motors
- What is a brushless DC motor?
- How do brushed DC motors work? The need for regular maintenance explained
- Brushless DC motor applications: examples that demonstrate their features
- Stepper motor applications: Examples that demonstrate their features
- Motors designed for easy control: How do stepper motors work?
- What are the differences between brushed and brushless DC motors?
- What is a PSC motor
- What is a servo motor?
- What is a blower?
- What is a DC motor? - features and mechanisms
Contact us for more information
- New inquiry
- Prototype
- Upgrade
- Customization
- Your spec
- Literature
- Support
- Others