What are the differences between brushed and brushless DC motors?
-
Automation
-
Health & wellness
-
Life environment
-
Automotive

2 Dec. 2020
DC motors can be divided into brushed and brushless motors. Brushed DC motors are equipped with a commutator and brushes, whereas brushless DC motors use an electronic circuit in place of these parts. What are the differences between these two types of DC motors?
This page explains the differences between brushed and brushless DC motors, and describes their respective advantages and disadvantages. For more information about DC motors in general, please visit the following page.
What is a DC motor? - Features and mechanisms
Applications for brushed and brushless DC motors
DC motors are used in a wide range of applications, from familiar household appliances to large industrial plants. Brushed DC motors in particular are among the most widely used of all types of electric motors, with uses ranging from the motors in toy models to auxiliary vehicle motors. Brushless DC motors also have a wide range of uses, including as components in the hard disk drives used to store data in PCs and in air conditioners, refrigerators, and other home appliances.
The choice of motor type depends not only on the application, but also on factors such as cost and maintenance. In terms of price, the requirement for an electronic circuit means that brushless DC motors tend to have a higher overall cost than brushed DC motors.
Brushless DC motors, on the other hand, have longer life as they lack the brushes and commutator that are in constant contact with each other in a brushed motor, and wear from friction. They also do not generate the electrical and acoustic noise that arises from this contact. This results in their being commonly adopted when you want to reduce the frequency of maintenance associated with routine parts replacement, or in applications that require quiet operation.
The commutator and brushes on brushed DC motors deteriorate with wear, causing them to have a shorter life than brushless DC motors. Nevertheless, brushed DC motors are sometimes chosen in applications where the aim is to keep the initial cost down and that allow for their replacement as consumable parts.
What is a brushed DC motor?
In a brushed DC motor, the coil is located in the rotor, which rotates in the motor’s magnetic field. This rotation causes the current flow in the coil to alternate in direction as the commutator contacts the alternate brushes. It is this alternation of current direction in the coil that causes the rotor to keep rotating, thereby driving the motor.
Brushed DC motors are divided into permanent magnet and electromagnet motors depending on the type of magnet used to provide the magnetic field.
Permanent magnet brushed DC motors are further divided into slotted, slotless, and coreless motors depending on the configuration of the armature (rotor).
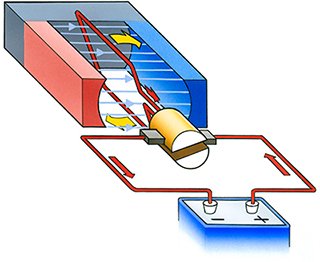
Electromagnet brushed DC motors use electromagnets to generate magnetic flux in place of a permanent magnet. This configuration is used for motors with medium to high output. They are further divided into distributed-winding, series-wound, and separately-excited motors.
The advantages of brushed motors are their simple configuration and ability to operate without an electronic drive circuit in applications where speed control is not needed.
Their disadvantage is that their brushes and commutator are consumable parts that require regular replacement. The brushes also generate electrical and acoustic noise.
What is a brushless DC motor?
A brushless DC motor avoids the need for a commutator and brushes by having its permanent magnets in the rotor. Rotation of the rotor is maintained by detecting the position of the rotor magnetic poles and switching the electric current flow through the coils accordingly.
This requires a drive circuit as the rotor will not turn by simply connecting the motor to a power supply.
Brushless DC motors are divided into surface permanent magnet (SPM) motors where the permanent magnets are attached to the outer circumference of the rotor, and interior permanent magnet (IPM) motors where they are embedded in the interior of the rotor.
Lacking the brushes and commutator found in brushed DC motors, the advantages of brushless DC motors include easier maintenance due to longer operating life, and quiet operation compared to brushed DC motors.
Factors to consider when choosing between brushed and brushless DC motors
Although they both use a DC power supply, brushed and brushless DC motors have different features and configurations. Brushed DC motors can be a choice in applications where the need for routine replacement of consumables is not a problem.
Because they do not require brushes and a commutator, brushless DC motors have a longer operating life and therefore easier maintenance than brushed DC motors, while also featuring quiet operation.
The choice of motor depends on what factors are important in the application, and should be made on the basis of a full understanding of their comparative features and performance.
Overcoming your problems with brushless DC motors
ASPINA supplies not only standalone motors, but also system products that incorporate drive and control systems as well as mechanical design. These are backed by comprehensive support that extends from prototyping to commercial production and after-sales service.
ASPINA can offer solutions that are tailored to suit the functions and performance demanded by a diverse range of industries, applications, and customer products, as well as your particular production arrangements.
ASPINA supports not only customers who already know their requirements or specifications, but also those who are facing problems at early stages of development.
Do you struggle with the following concerns?
Motor selection
- Don't have detailed specifications or design drawings yet, but need advice on motors?
- Don't have anyone in-house with expertise in motors and can't identify what sort of motor will work best for your new product?
Motor and associated component development
- Want to focus your resources on core technology, and outsource drive systems and motor development?
- Want to save the time and effort of redesigning existing mechanical components when replacing your motor?
Unique requirement
- Need a custom motor for your product, but been declined from your usual vendor?
- Can't find a motor that gives you the control you require, and about to give up hope?
Seeking answers to these problems? Contact ASPINA, we're here to help.
List of the same series columns
- Applications for blower motor
- What is a blower motor?
- Advantages of brushless DC motors over brushed DC motors
- Features and applications of DC motors
- Is this brushless motor cheap or expensive? - What factors determine its price?
- Different types of DC motor and their respective features
- What is a geared brushless DC motor?
- How does an electronic speed controller for a brushless DC motor work? And what should you consider when you choose the right one?
- Small brushless motors
- Difference between brushed motor and brushless motor
- What are the disadvantages of brushless DC motors? And how can they be overcome?
- Advantages of brushless DC motors: How they differ from brushed DC motors
- What is an actuator?
- How do brushless DC motors work? The need for a drive circuit explained
- Do brushless DC motors require a drive circuit? – Controlling brushless DC motors
- What is a brushless DC motor?
- How do brushed DC motors work? The need for regular maintenance explained
- Brushless DC motor applications: examples that demonstrate their features
- Stepper motor applications: Examples that demonstrate their features
- Motors designed for easy control: How do stepper motors work?
- What is a PSC motor
- What is a servo motor?
- What is a blower?
- What is a DC motor? - features and mechanisms
Contact us for more information
- New inquiry
- Prototype
- Upgrade
- Customization
- Your spec
- Literature
- Support
- Others