ASPINA’s new servo motors enhance competitiveness in medical device development
-
Health & wellness
-
Syringe pump
-
Rehabilitation
-
Laboratory analysis systems
-
Centrifuge
-
Conveyor
Motor performance required for today’s evolving medical devices
ASPINA is developing servo motors specifically for medical equipment in the 100 to 400 W output range. This product line is intended to address the needs of medical device manufacturers who require adequate performance without excessive cost or unnecessary system complexity. The motors operate at 24 to 48 V, enabling compliance with low‑voltage safety requirements while maintaining flexibility in system‑level design.
Recent medical systems have become increasingly sophisticated. Examples include surgical robots that require precise low‑speed motion and fine positioning, syringe pumps that must achieve micro‑flow delivery with stable speed regulation, and diagnostic analyzers that process micro‑samples with high sensitivity and continuous duty operation. These devices rely on motion subsystems capable of accurately controlling complex mechanical assemblies.
As a result, motor selection plays a critical role in determining the overall performance, safety, and reliability of medical equipment, particularly in applications requiring position or speed control. To support these needs, ASPINA continues to advance servo motor designs optimized specifically for medical applications.
A motor solution targeting the unmet performance requirements in MedTech motion control
In general, servo motors used for industrial machinery are designed for applications involving heavy loads and high throughput, which drives the need for very high resolution, high dynamic performance, and corresponding system cost. When such industrial motors are used in medical equipment, they frequently exceed the performance actually required, resulting in over‑specification and unnecessary cost. On the other hand, medical device engineering teams must meet medical‑specific safety and reliability constraints and certification hurdles not standard for industrial motors, which complicate design and prolong validation. These factors make motor selection more challenging for medical device manufacturers.
ASPINA’s Medical Engineering Business Unit initiated a servo‑motor lineup purpose‑built for medical devices in the 100 to 400 W class. By rightsizing the encoder resolution and feature set, the design increases architectural freedom and reduces cost. Low‑voltage (24 to 48 V) operation further improves safety and simplifies the engineering pathway to compliance.
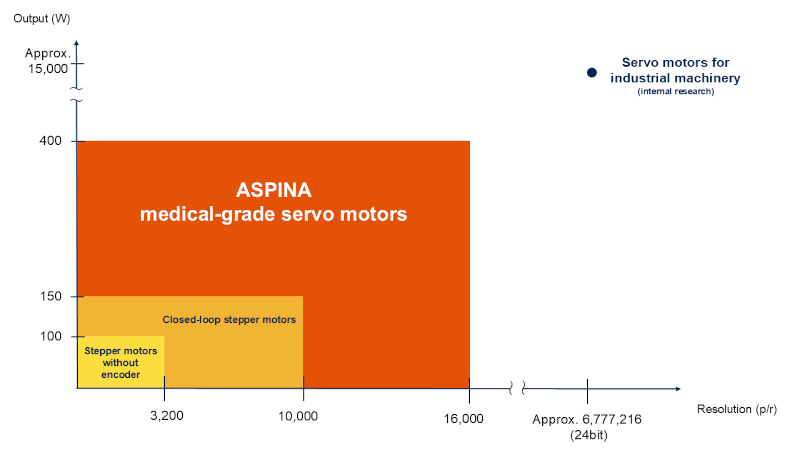 Positioning of ASPINA’s servo motors for medical devices in the output‑performance landscape
Positioning of ASPINA’s servo motors for medical devices in the output‑performance landscape
ASPINA servo motor architecture optimized for medical-device integration
ASPINA’s architecture combines a BLDC motor with Hall ICs and a magnetic encoder, rather than relying on optical encoders typical of high‑end industrial systems. This choice balances precision, robustness, cost, and integration simplicity for medical environments.
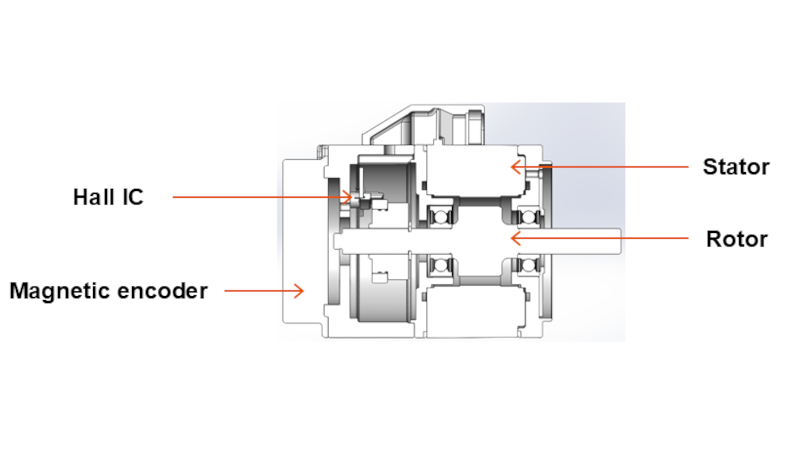 Cross‑sectional structure of ASPINA’s servo motor for medical devices
Cross‑sectional structure of ASPINA’s servo motor for medical devices
Encoder resolution and control characteristics for medical‑grade motion accuracy
The magnetic encoder provides approximately 16,000 counts per revolution. This resolution is adequate for medical‑grade position and speed control, avoiding the cost and complexity of multi‑million‑count optical encoders that are unnecessary in many medical mechanisms.
BLDC motor + magnetic encoder configuration enabling system‑level design flexibility and cost reduction
The BLDC motor with Hall ICs and a magnetic‑encoder stack enables servo‑like control at a lower system cost than conventional industrial servo solutions. Depending on accuracy requirements, the motor can be deployed with servo control or as a motor‑only configuration. Motor‑control functions can be embedded on the product’s main PCB, enabling tighter system integration and reduced component cost.
SELV‑based low‑voltage drive design supporting medical safety compliance
In medical devices, safety is always the top priority and the insulation requirements needed to ensure this safety depend largely on a device’s operating voltage. ASPINA’s servo motors for medical equipment operate at 48V or below, falling within the Safety Extra Low Voltage (SELV) range. As a result, insulation requirements such as clearance and creepage distances and insulation thickness are less strict than those for high-voltage motors. This not only reduces the risk of electric shock but also makes it possible to design more compact devices. Using components within the SELV range can also simplify the process of complying with medical standards like IEC 60601, making it more straightforward than working with high-voltage systems.
The table below summarizes the key differences between SELV and high‑voltage systems, focusing on shock risk, regulatory effort, fault behavior, and design complexity.
| SELV | High voltage systems | |
|---|---|---|
| Electric shock risk | Very low | Higher |
| Standards alignment | Easier path to IEC 60601, JIS T 0601, etc. | Additional mitigations required |
| Single fault safety | No hazardous voltage under single fault | Potential hazardous voltage |
| Patient safety | High | Additional insulation/isolation required |
| Design complexity | Moderate (isolation/segregation still needed) | High (multi layer safety measures) |
Japan-made manufacturing quality and stable supply for medical devices
ASPINA manufactures these servo motors in our Japan factory, which is managed under an ISO 13485‑compliant quality management system. The result is stable, traceable production aligned with regulated medical markets helping our customers reduce procurement risk and ensure continuity across the device lifecycle.
ASPINA’s servo motors: Engineering advantages for medical device development and development specifications
ASPINA’s medical‑grade servo motors eliminate the need to purchase expensive servo systems. They offer high design flexibility, simplified compliance with safety standards due to low‑voltage operation, reduced development and procurement costs, shortened development cycles, and a reliable long‑term supply.
 ASPINA’s medical‑grade servo motors
ASPINA’s medical‑grade servo motors
The table below shows the key development specifications of the ASPINA servo motors.
| Size | □60 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rated voltage [V] | 48 | ||
| Rated Speed [RPM] | 3500 | ||
| Rated output [W] | 100 | 200 | 400 |
| Rated torque [N·m] | 0.273 | 0.546 | 1.091 |
| Rated current [A] | 2.6 | 5.2 | 10.4 |
Current development is centered on the □60 frame. The lineup will be expanded with □40 (compact) and □80 (high‑power) models to cover smaller footprints and higher‑power mechanisms.
ASPINA supports not only motor provision but also drive circuitry and control design proposals. The organization is structured to assist medical device manufacturers from concept through mass production.
ASPINA’s medical servo motors are intended to accelerate the evolution of medical devices, enable innovation at the point of care, and improve quality of life globally. For detailed specifications or technical inquiries, please contact us.